INDOOR AIR QUALITY: Health in the building
A healthy environment in buildings

Air quality, who is it for?

| Territory |
|

| Buildings |
|

| Occupants / Operators |
|
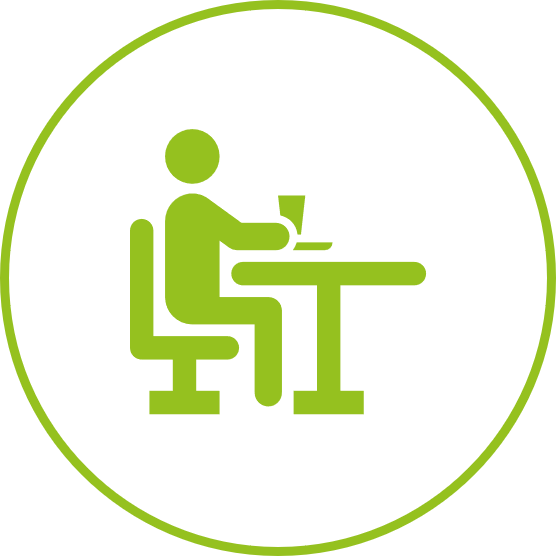
How to take into account the indoor air quality?
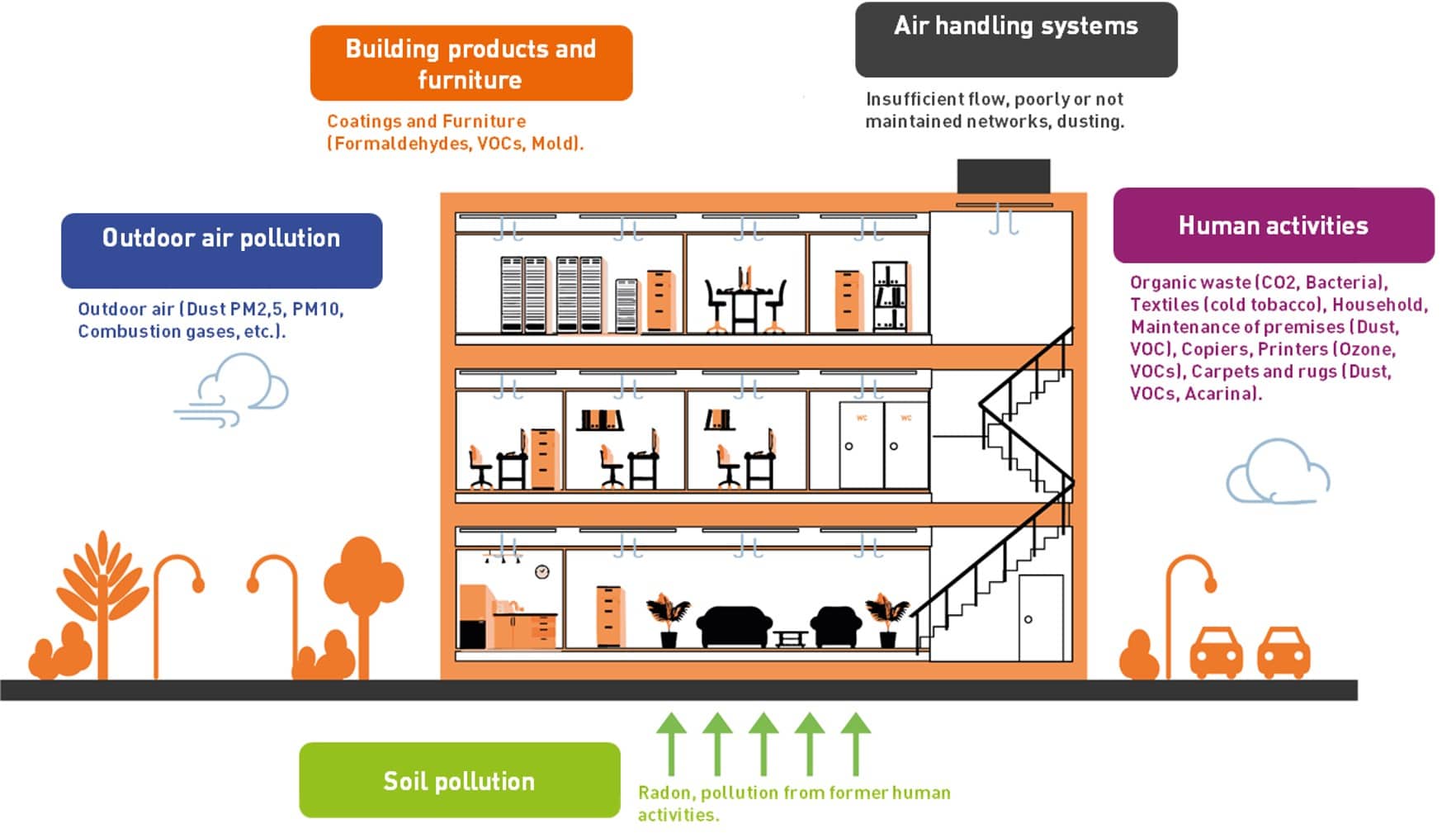
How to measure indoor air quality?

| Passive Measures |
|

| Active Measures |
|

| Monitoring |
|
How to depollute indoor air?
Trapping technique
HEPA Filtration: System for trapping gas molecules such as VOCs or NO2 on a filtrate.
Activated Carbon Filtration or Impregnated Filter: Transformation of an electrically neutral element into an ion (charged species) allowing them to be captured more easily on surfaces.
Ionization / Electrostatic Precipitation: Use of an electrical discharge that separates the oxygen atoms in the air and creates ozone. This reacts with the pollutants in the air.
Oxidation or destruction
Ozone: The use of an electrical discharge that splits the oxygen atoms in the air and creates ozone. This reacts with the pollutants in the air.
UV: UV radiation can destroy bacteria and certain pathogens in the air by breaking down the DNA of these organisms.
Photocatalysis: Compilation of a catalyst like titanium dioxide and light radiation creating oxidation-reduction reactions until degradation of the pollutants present in the air.
Plasma: Mineralization of organic molecules through oxidation reactions initiated by free radicals produced in an ionizing field.
Air quality and COVID-19